What is cognitive automation?
Cognitive automation is part of the digital fabric that is predominantly weaved with technologies like AI and ML to drive automation at an enterprise-wide level that is capable of thinking like humans along with mimicking human behavior.
Digital Fabric, “It is the combination of technologies enabling automation to serve dynamic business needs of organizations that seek digital transformation to enhance business outcomes.”
Cognitive automation leverages a set of interwoven technologies such as speech recognition, natural language processing, text analytics, data mining, and semantic technology. By integrating multiple systems across various functional areas, cognitive automation can implement intelligent process automation capable of handling exceptions, capture and utilize data, automate data-driven decision making, and scale operations.
Why should enterprises embrace cognitive automation?
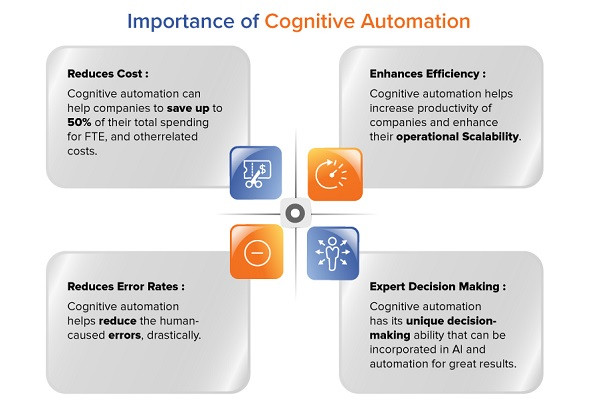
Businesses, to sustain themselves in today’s competitive digital era, must innovate, scale and grow at a rapid pace. Data is critical and forms the foundation for business growth. However, more than 60% of organizational data is either semi-structured or unstructured.
Traditional RPA-based automation is used to automate repetitive, mundane, and time-consuming tasks that mostly work with structured data. Moreover, RPA still requires significant human intervention to make informed decisions, supervise workflows, evaluate the output of any system, and the like. It cannot simulate human intelligence to perform contextual analysis as well as handle contingencies. It best performs uninterrupted, repetitive actions based on a predefined set of rules.
In contrast, intelligent cognitive automation can work on structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data to enable process automation of highly complex operations. It can handle vast volumes of unstructured data to analyze, process, and structure into data that is appropriate for the successive steps of any given operation.
It deploys cognitive algorithms that infuse cognitive ability to identify requirements; establish connections between unstructured data, sporadic events, anomalies, and the like. Cognitive automation contextually analyses the data in hand to automate processes, handle exceptions, forecast outcomes, as well as provide stakeholders with real-time organizational data to make data-driven decisions.
Live cognitive automation use cases
Cognitive automation is fast becoming mainstream and is implemented to develop self-servicing business paradigms. With its limitless technical possibilities and immense scope, it is widely deployed across multiple verticals such as in front, middle and back-office operations, IT, HR, finance as well as marketing and sales.
Let’s discuss few imperative use cases spanning across different industries:
1) INDUSTRY - Finance
Use Case: Financial Advisory
The global financial market has seen a surge in budget management apps based on cognitive process automation that caters effective, specialized, and targeted financial advice as well as guidance to a wide spectrum of customers. These apps aid customers in tracking and monitoring their day-to-day spending, learning about their purchasing behavior and patterns, as well as draw inferences on where they can save.
Robo-advisors are another prevailing trend in this domain. Robo-advisors particularly target investors with limited resources like individuals, SMEs, and the like, who seek professional guidance to manage their funds. Intelligent automation powered robo-advisors build financial portfolios as well as comprehensive solutions like trading, investments, retirement plans, and others for their customers.
2) INDUSTRY - Software / Information Technology sector
According to the latest technology trends, the software industry is heavily dependent on intelligent process automation solutions and they are widely used by the testing community, service organizations, and testing product/tools firms to list a few.
A popular technical theme called “Codeless Functional Test Automation” has found extensive scope in the software testing domain. Here, after the test environment has been automated, the test engineers allow the configured systems to figure out how to automate the software product under test. Many automated testing tools have been developed and deployed in this domain that makes exhaustive testing possible, a feat that can never be accomplished with manual testing.
Furthermore, cognitive automation platforms minimize testing efforts while enhancing test coverage.
3) INDUSTRY - Retail
Use Case: Product recommendations based on customers’ buying behaviors
To assist customers fruitfully retailers require every customer to maintain individual accounts both at the physical store as well as online. With personal shopping accounts enabled, retailers offer amenities such as pickups, deliveries, and loyalty points. This data aids the shopkeepers to personalize each customer’s preferences. Cognitive algorithms scour tons of data to identify products purchased, combinations preferred, sought-after brands, buying capacity, and shopping frequency. Cognitive process automation accurately predicts customers’ needs and forecasts their next visit for specific requirements.
Closing Thoughts:
In this era of unprecedented technical advancements, every enterprise is weaving its transformation into a digital fabric to meet its business needs. The digital fabric to be implemented should mind the sunk cost of your existing technologies and build a dynamic framework to adopt newer technologies for exponential growth and increased ROI, there is no ‘one size fit all’ strategy when automation comes into the picture.
Cognitive automation with its industry-oriented solutions and business-driven approach is inevitable. Though it isn’t a comprehensive solution, it forms a critical component in providing enterprises with a framework consisting of well-defined workflows, process automation, and the like. It fulfills immediate needs, mid-term, and long-term business goals too. The ability to construct business workflows by interweaving unstructured data from various sources like documents, customer interactions, videos, voice, and machine vision as well as from emails, emerges as its primary benefit.
Furthermore, intelligent cognitive automation is developed so that it can be used by business users with ease without the assistance of IT staff to build elaborate models. It utilizes new data that are fed into the system most harmoniously. It builds more connections in the datasets allowing intuitive actions, predictions, perceptions, and judgments. This digital fabric is weaved to outshine other technologies with its capability to imitate human thinking thus learning the intent of a given process and adapting accordingly.